Java RabbitMQ发布订阅模式(广播模式、fanout模式),使用的交换机类型为FanoutExchange,就是一个生产者发送的消息会被多个队列的消费者处理,架构如下图
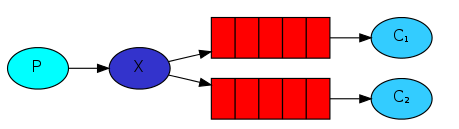
Fanout交换机可以将消息转发给所有绑定的队列。
提示:无论使用RabbitMQ那种工作模式,区别就是使用的交换机(Exchange)类型和路由参数不一样。
1.前置教程
请先阅读下面章节,了解相关知识
- RabbitMQ基础概念
- RabbitMQ 发布订阅模式
- RabbitMQ Java快速入门章节 (必读,因为后续章节不会重复贴代码,仅展示关键代码)
2.定义Fanout交换机
在Spring AMQP中Fanout交换机对应的类就是FanoutExchange,我们通过Springboot配置类,定义交换机。
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
// 定义交换机
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanout() {
// 参数为交换机名字,不能重复
return new FanoutExchange("tizi365.fanout");
}
}
提示: 无论是消息生产者还是消费者都需要交换机。
3.发送消息
我们将消息发送给交换机,由交换机根据路由规则投递消息到对应的队列。
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SendService {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
@Autowired
private FanoutExchange fanout;
// 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000)
public void send() {
// 消息内容
String message = "Hello World!";
// 发送消息
// 第一个参数是交换机名字
// 第二个参数是路由参数,fanout交换机会忽略路由参数,所以不用设置
// 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化
template.convertAndSend(fanout.getName(), "", message);
System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'");
}
}
4.接收消息
4.1.定义队列&绑定交换机
要想消费队列消息,需要先定义一个队列,然后将队列绑定到目标交换机上。
下面定义两个队列,分别绑定到同一个交换机上
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanout() {
// 定义交换机
// 参数为交换机名字,不能重复
return new FanoutExchange("tizi365.fanout");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue1() {
// 定义队列1
return new Queue("tizi365.fanout.queue1");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue2() {
// 定义队列2
return new Queue("tizi365.fanout.queue2");
}
@Bean
public Binding binding1(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue queue1) {
// 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到fanout交换机上
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(fanout);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding2(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue queue2) {
// 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到fanout交换机上
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(fanout);
}
}
4.2.定义队列监听器
通过RabbitListener注解定义消息监听器,消费指定队列的消息。
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 将当前类交给Spring管理
@Component
public class DemoListener {
// 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.fanout.queue1")
public void receive1(String msg) {
System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg);
}
// 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.fanout.queue2")
public void receive2(String msg) {
System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg);
}
}
因为前面定义交换机(exchange)的时候使用的是fanout类型,所以每一条消息,都会分发给所有绑定到当前交换机的队列中,消息会被上面的两个方法分别处理。
提示:RabbitListener注解可以作用在类上,也可以作用在方法上,如果RabbitListener注解定义在类上,则需要配合RabbitHandler注解标记由那个类方法执行消息处理。
4.3.全注解方式定义队列监听器
不需要前面的springboot配置类定义交换机、队列和绑定关系。
直接通过RabbitListener注解的bindings参数定义绑定关系、队列、交换机。
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "tizi365.fanout.queue3", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "tizi365.fanout", durable = "true",type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT)
)
}
)
public void receive3(String msg) {
System.out.println("收到队列3的消息 = " + msg);
}
说明:
- QueueBinding注解:定义队列和交换机的绑定关系,value参数用于定义队列,exchange用于定义交换机
- Queue注解:定义一个队列,name参数定义队列名(需要唯一), durable参数表示是否需要持久化
- Exchange注解:定义一个交换机, name参数定义交换机的名字,type参数表示交换机的类型